
Jul 21, 2022
0 Comment by ViewersA geographic information system (GIS) is a system that creates, manages, analyzes, and maps all kinds of data. GIS interfaces data to a map, integrating location data (where things are) with all kinds of enlightening information (what things are like there). This gives a foundation to mapping and analysis that is utilized in science and almost every industry. GIS assists clients with understanding patterns, relationships, and geographic setting. The advantages incorporate superior communication and effectiveness as well as better management and independent direction.
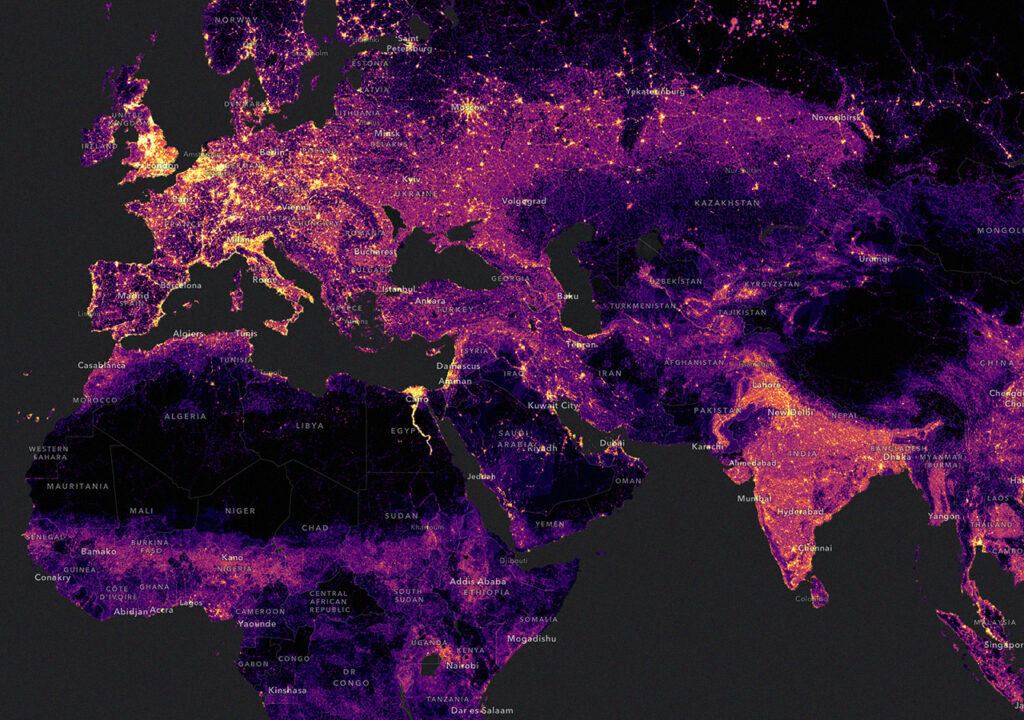
Countless organizations in virtually every field are utilizing GIS to make maps that communicate, perform analysis, share information, and take care of complicated issues around the world. This is changing the way the world works.
Illuminate issues that are driven by geography. In this story, maps and visualizations connect present-day environmental inequalities to redlining policies.
Visualize and communicate change. This story uses maps to show how humans impact our warming planet and shares what we can do to create a more sustainable future.
GIS delivers real-time situational awareness. The maps in this story help us understand the spread of COVID-19 and the global impact of the pandemic.
By analyzing soil health, farmers can determine when and where to plant certain crops, maximizing yield while minimizing environmental impact.
Visualize data with GIS to gain insights that might be missed in a spreadsheet. This story uses maps to understand bird populations and migration routes.
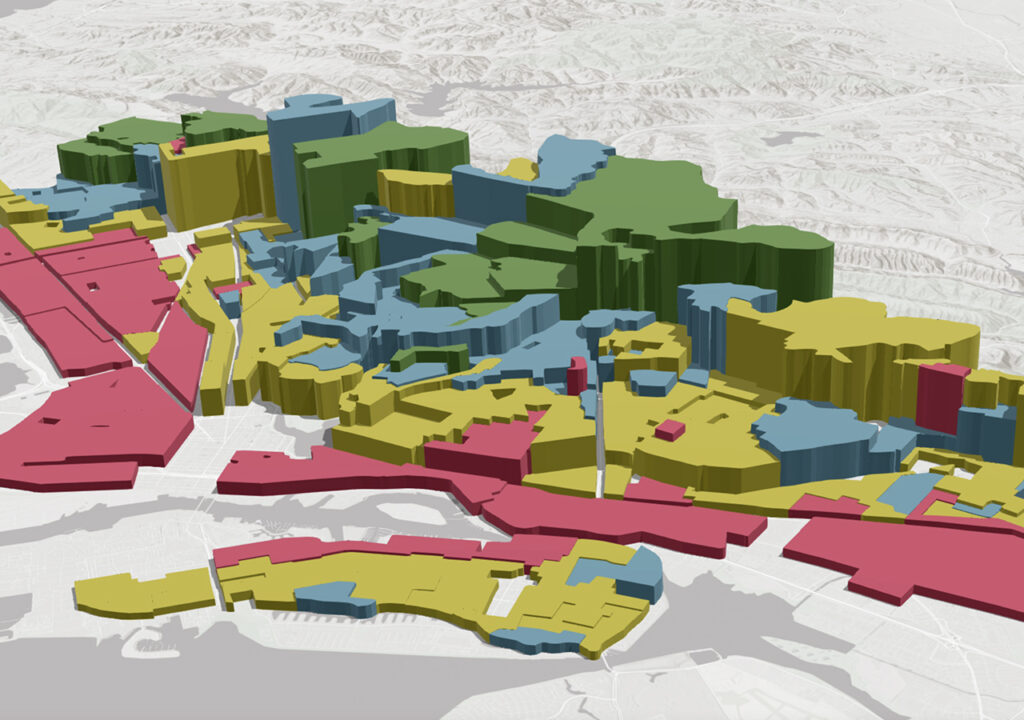
GIS technology applies geographic science with tools for understanding and collaboration. It helps people reach a common goal: to gain actionable intelligence from all types of data.

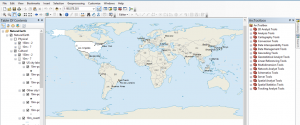
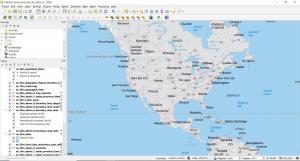
ArcGIS Pro modernizes GIS with a ribbon interface, 64-bit processing, and 3D integration. It’s a massive overhaul with a focus on quickness, ingenuity, and cartography. Even though ArcGIS Pro is a big machine with lots of moving parts, it earns the top spot.
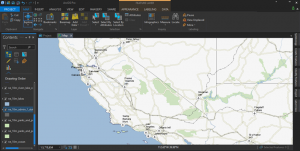
Open source flows in the DNA of QGIS 3. It’s been genetically tailored to break the mold of commercial GIS with equally superior cartography, editing, and analysis tools. It’s not only a great choice because 3D is native as part of QGIS 3. But QGIS plugins still give you the power to analyze with almost endless capabilities.
ArcGIS Desktop is cutting edge in GIS. It raises the bar to the next level by doing what other GIS software can’t. Its success is that it’s expandable. From field apps to modeling and scripting, ArcGIS Desktop is a powerhouse for all things GIS.
Hexagon GeoMedia has 40+ years of history. But lately, it’s taken a bit of a slide. Nevertheless, Geomedia is still solid as GIS software. Especially, when you pair it up with ERDAS Imagine, you get arguably the best suite in remote sensing.
At its core, MapInfo Professional is all about locational intelligence. And just like GeoMedia, it’s been a tale of shrinking market share from its rivals. But don’t get fooled. MapInfo Professional is still a well-rounded GIS software suite with more of a business decision-making focus.
Read More About: GIS Mapping Tools: How They Work